Thursday, August 20, 2009
Conductive Keratoplasty
Saturday, August 15, 2009
Radial Keratotomy
The patient is diagnosed with myopia and astigmatism (uneven cornea surface). Other than that, the eyes are normal, healthy with stable, mild to moderate myopia (up to 3 diopters). This patient will be eligible for Radial Keratotomy (RK) if he/she does not have pathological myopia, in which the eyeball fails to stop growing longer. Degenerative changes caused by severe nearsightedness (high myopia), such as retinal tears and abnormality or disease of the cornea should not be present in the eyes.
Usually, the patient is given the option to choose between several other types of operations. Photorefractive Keratotomy (PRK) and LASIK surgery have replaced RK by popular choice, yet it is still effective in reducing mild myopia.
Process #1
The eye is anesthetised and a ring is fixed to it in order to prevent if properly positioned and flat.
A precision calibrated diamond knife is used to make four to eight incisions perpendicular to the circumference of the cornea. To achieve high efficiency, the incisions usually reach deep into the cornea. This will cause the cornea to flatten and thus change the shape of the lens.
Recovery and results
RK causes more discomfort and requires a much longer time to heal as compared to PRK and LASIK. The results are also more unpredictable. However, the incisions are suspected to never heal entirely. There have been reports of unhealed incisions even after 20 years of surgery. These open wounds allow bacteria to settle and spread, thus causing much more harm like infections and inflammation to the eye. Therefore, patients have to return to doctors frequently for the first year in order to prevent these damages.
Possible Side-effects
-More scattering of light
-Loss of fine depth perception
-Puncture of the cornea
-Infection
-Inflammation
-Glaucoma
This surgery is still being performed albeit less popular than PRK and LASIK.
Sources
http://www.webmd.com/eye-health/radial-keratotomy-rk-for-nearsightedness
http://www.docshop.com/education/vision/refractive/other-treatments/
Laser Thermal Keratoplasty surgery
· Uses a Holmium laser (an infrared laser that emits heat to reduce the size of the corneal tissue) to reshape the cornea for correction of low ranges of hyperopia (farsightedness).
· The Holmium laser gently heats stromal collagen in a circle around the outside of the pupil. The heat results in the tissue becoming much smaller, forming a tightening effect.
· The side of the cornea is pulled, causing the center to protrude. Because the cornea of a farsighted eye is too flat, this bulging effect, when carefully controlled, corrects the problem.
Use of LTK procedure
- Treat people who are far-sighted.
Advantages
- Quick
- Simple
- Causes little pain
- Low rate of infection
- The recovery period is also much quicker, usually only taking around 2 days
Side-effects of LTK procedure
- After LTK surgery, subsequent appointments are needed for the very next day and for one week, one month, and 3-6 months after the procedure.
- Even an object in your eye may be felt for the first 24 hours following LTK.
- Eye drops can help relieve this, but only to a certain extent.
- Light sensitivity may also be felt for the first 24 hours and sunglasses may be advisable.
http://www.healthcentre.org.uk/laser-eye-surgery/laser-thermal-keratoplasty.html
http://www.visionrx.com/Library/enc/enc_ltkeratoplasty.asp
www.visionrx.com/library/.../innov_laser_thermal.asp
http://www.youreyeguide.co.uk/ltk/ltk-sideeffects-aftercare.html
http://www.urologicinstituteofnj.com/images/stonesLaser.jpg
http://www.visionrx.com/library/enc/tableac.asp
Friday, August 7, 2009
Mindmap
Consequences if surgery is not proceeded properly
- Keratectasia - When a surgeon accidentally operates too deeply in the eye, the cornea will become altered and the patient may become blind.
- Irregular Astigmatism - If laser rectification is not properly performed or when the eye is rough. The patients suffering from this error require more operation instead. At times seeing double is a result of a little inflammation.
- Dry eye – This condition is generally common, but can be easily solved by eye drops.
- Night Vision Problems – Such problems occur when doctors utilise conventional LASIK methods. The implication of night vision problems consists of many. One of the problems is blurry sight (glare and halos around objects). Distorted vision can happen at daytime too. However, at night it turns much more obvious and troublesome.
- Over or under correction - Blurry vision or very slight seeing difficulties. Most of the time patients put on contact lenses or spectacles to correct this complication. Undergoing re-treatment is also an option.
http://www.lasikeyesurgerycorrection.com/lasik_risks.html
http://www.webmd.com/eye-health/night-vision-problems-halos-blurred-vision-night-blindness
Thursday, August 6, 2009
Mindmap
.jpg)
Mindmap consisting of all the processes, side-effects of ALK and PKR surgeries as both are more common. Side-effects as shown by LASIK is compared with our findings.
Results of surgeries
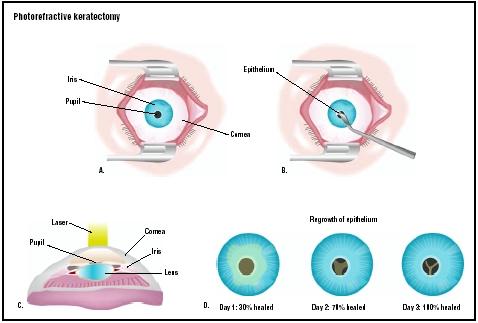
Photorefractive Keratectomy Surgery
Photorefractive keratectomy is a refractive medical operation that does not involve the use of tools in the human body whereby the doctor uses an excimer (a stable atomic pair dimer in which one of the two bound atoms is in a higher energy state) laser to reconstruct the cornea by taking away the epithelium, the jelly-like exterior layer of the cornea.
Purpose
Although PRK decreases nearsightedness (myopia), farsightedness (hyperopia), and astigmatism (blurred vision), this surgery can best take care of myopia. People who have undergone PRK usually do it for many different reasons. A most common reason would be that people do not want to wear spectacles because they want to appear handsome or beautiful. Others who take part in lots of sports or physical training may find spectacles a great hindrance. Moreover, contact lenses often dry up, leaving people with blurred vision.
Process
The whole process is approximately 10 minutes. Directly ahead of the operation, the ophthalmologist will execute a refraction to ensure the refractive alteration the surgeon will instruct the excimer laser is right. Anesthetic drops will be used to numb the eye and disallow pain when the operation starts. After the eye drops are applied, the surgeon places a speculum in the eye to keep the eyelids apart and disallow movement. The patient stares at the twinkling light of a laser microscope and must keep his or her gaze steady on that light, staying motionless at the same time. The surgeon rechecks the laser co-ordinates to ensure they are right for the refractive mistake. When everything is in position, the eye surgeon takes away the epithelium with a sponge, mechanical blade, or the excimer laser. With the epithelium totally taken away, the surgeon will start reconstructing the cornea. Once the process is done, the surgeon puts a bandage contact lens on the treated eye to protect it and allow the healing process to take place; it also eases some of the pain of the exposed cornea. The surgeon will also dispense anti-inflammatory and antibiotic eye drops to stop infection and reduce pain.
Risks
Patients should have a complete eye evaluation and medical history taken before surgery. Soft contact lens wearers should stop wearing their lenses at least one week before the initial exam. Gas-permeable lens wearers should not wear their lenses from three weeks to a month before the exam. Contact lens wear alters the cornea's shape, which should be allowed to return to its natural shape before the exam. Patients should also disclose current medications. Allergy medications and birth control pills have been known to cause haze after surgery. Physicians will want to examine the potential risks involved with these medications. Patients who have these conditions/history should not have the procedure, including:
- pregnant women or women who are breastfeeding
- patients with very small or very large refractive errors
- patients with scarred corneas or macular disease
- people with autoimmune diseases
- diabetics
- glaucoma patients
- patients with persistent blepharitis
Physicians will perform a baseline eye evaluation, including a manifest and cycloplegic refraction, measurement of intraocular pressure (to determine if the patient has glaucoma), slit-lamp biomicroscopy, tear film evaluation, corneal topography, evaluation of corneal thickness, dilated fundus examination, and measurement of scotopic pupil size. If the patient is an appropriate candidate, he or she must sign an informed consent form that states he or she is aware of possible complications and outcomes of the procedure.
PRK patients may experience glare, vision fluctuation, development of irregular astigmatism, vision distortion (even with corrective lenses), glaucoma, loss of best visual acuity, and, though extremely rare, total vision loss. A more common side effect is long-term haze. Some patients who have aggressive healing processes can form corneal scars that can cause haze. With proper screening for this condition and with the use of eye drops, this risk can be lessened. Complications associated with LASIK, such as photophobia, haloes, and dry eye, are not as common with PRK. However, the patient may be under-corrected or overcorrected, and enhancements might be needed to attain the best visual acuity.
Sources:
http://www.surgeryencyclopedia.com/Pa-St/Photorefractive-Keratectomy-PRK.html
Wednesday, August 5, 2009
Automated Lamellar Keratoplasty
The patient is diagnosed with severe levels of myopia or mild levels of hyperopia (farsightedness). To provide the custom treatment for the severity of the patient’s eye(s), the doctor will evaluate the medical history including glasses’ prescription, if any, and measure the corneal thickness, refraction and pupil dilation of the eye(s). This is required to determine the shape to cut which will restore perfect vision for the eye(s). Also, a coordinator will discuss with the patient about what to expect after the surgery.
Preparation for doctors
To begin the operation, the doctors have to prepare a device called a microkeratome which removes a thin disc of the cornea. More importantly, doctors have to calculate the shape to cut according to the patient’s eye(s). Other things include anaesthesia and the operation room itself.
Process #1
The eye is anesthetised and a ring is fixed to it in order to prevent if properly positioned and flat.
The microkeratome is used to incompletely cut a thin flap of cornea so as to expose the layer of tissue below. Then, the microkeratome is used again to carve the right shape in the cornea so as to change the shape of the eye lens. The flap is then replaced for it to heal. However, if the patient is hyperopic, the flap is replaced back without removing anything. This is because the cornea stiffens during recovery. This operation usually takes less than an hour.
Recovery and results
Just 24 hours after the operation, patients are almost healed and able to see clearly. Besides, patients feel very comfortable after the surgery although it may take months to regain vision stability. The results may sometimes be unpredictable, but ideally, the patient will have perfect vision after the surgery.
Possible Side-effects
Glare
Inability to wear contacts, sometimes permanently
Infection
Corneal scarring
Overcorrection or under-correction
Inflammation
Due to presence of more predictable and efficient types of operations, this type of surgery is not routinely performed anymore.
Sources
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Automated_lamellar_keratoplasty
http://www.webmd.com/eye-health/keratoplasty-eye-surgery-alk-myopia-hyperopia
http://www.the-lasik-directory.com/alk.html
http://www.eyecare-information-service.org.uk/lasereyesurgery/alk.html
Tuesday, July 21, 2009
Edited Research Question
Problem Statement: How accurate risks of surgeries shown by LASIK and how effectively are they conveyed?
We thought that it would be good to research on the dangers of Lasik as not many people know the procedure well since the information provided by LASIK might be limited or inaccurate as they would want to cloud some of the information as not to scare of their patients. We would also need to find out how strongly does LASIK enforce their patients awareness and knowledge in what they themselves are going through and the risks they are taking.
What we intend to do:
We intend to find out about how the Lasik treatment will affect the person’s eyes and even health and compare it with the information provided by LASIK, hence, changing the information in their advertisements or brochures, which are supposed to educate the public, so that the patients have a clearer view of what they are going through. We would also need to find out how knowledgable patients really are when they accept these surgeries so as to know LASIK's enforcement on the patients' awareness.
Tuesday, July 14, 2009
Research Question
- Reflection
-- How did the group come up with the problem statement?
-- What did you do well? e.g. difficulties faced and were overcome, how you overcome them
-- What did you not do well? e.g. difficulties that have yet to overcome due to some barriers
-- What you intend to do?
Problem Statement: What are the risks of lasik?
We thought that it would be good to research on the dangers of Lasik as not many people know the procedure well.
We had problems trying to create the mindmap as it needed a lot of details thus we just had to split the work up. However, we were able to collate everything and the mindmap was understandable.
We think our group had a hazy out view of the whole project because there are plenty of risks involved in Lasik.
We intend to find out about how the Lasik treatment will affect the person’s eyes and even health and whether a Lasik procedure is worth it, both to the person’s well-being and money.



.jpg)

.png)

